2024 Best 3D Laser Scanner Buying Guide
3D laser scanning technology is rapidly becoming a prominent topic in today’s market, with increasing demand across various industries.
This technology accelerates the creation of digital models during engineering, design, and manufacturing processes, and is also used for quality control in post-production.
So, what exactly is a 3D laser scanner? What are its specific applications? How do you choose the right 3D laser scanner for your needs?
As 3D laser scanning technology advances, its applications are expanding, providing new tools for data collection and processing. This article will address these questions in detail, helping you make an informed decision when purchasing a 3D scanner.

What is a 3D Laser Scanner?
A 3D laser scanner is a non-contact, non-destructive device that uses laser technology to precisely capture three-dimensional data of objects.
During the scanning process, the laser projects encoded light patterns that match the shape of the object, thereby generating a digital model of the object.
These digital models can be exported as polygon mesh files and are widely used in computer-aided design (CAD), inspection, and 3D printing applications.
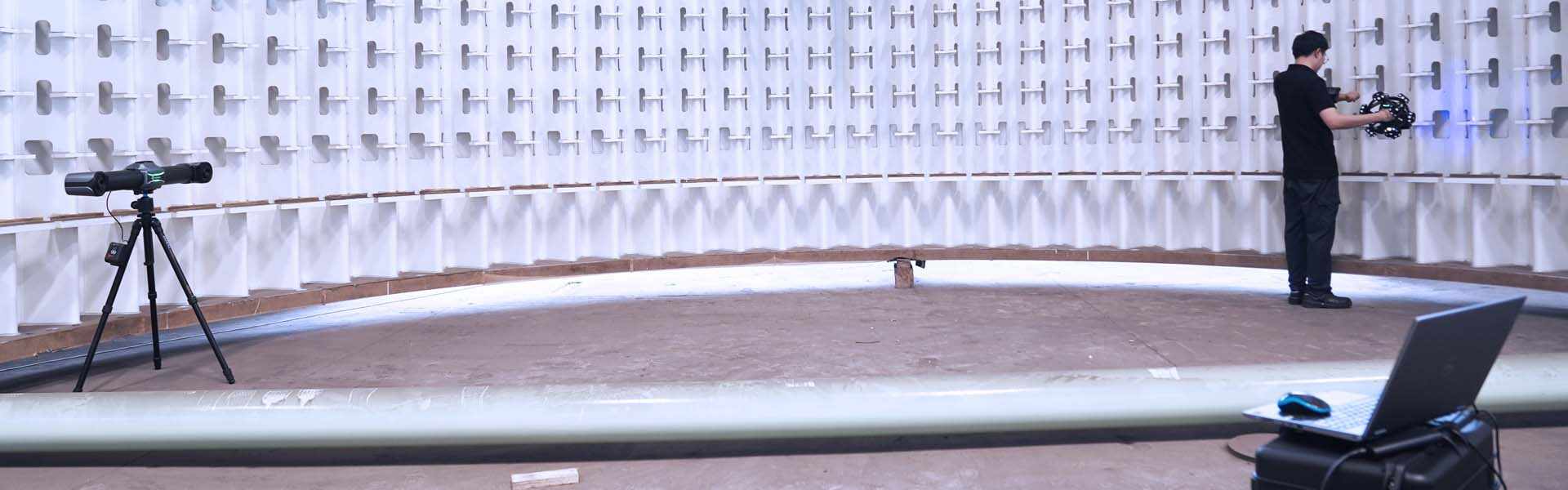
3D laser scanning systems are suitable for various scenarios including architecture and industrial inspection. These systems efficiently capture high-precision 3D point cloud data and quickly generate realistic 3D models.
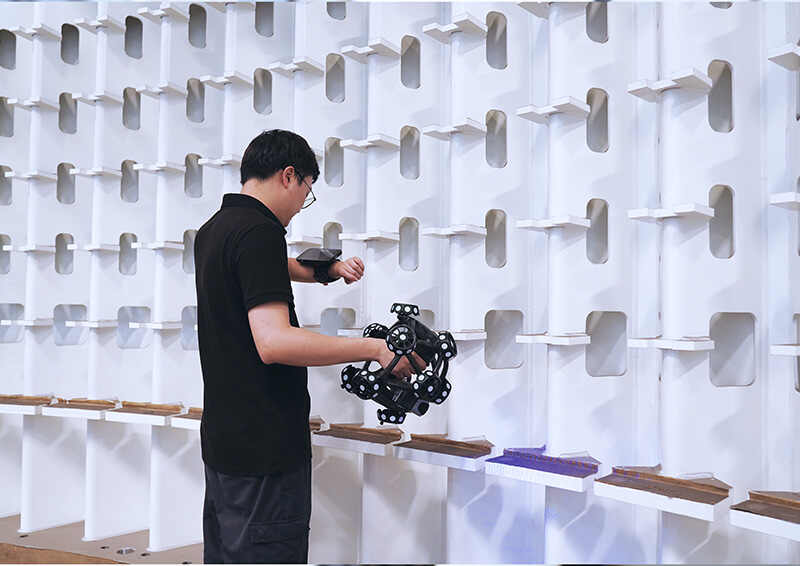

What is a Handheld 3D Laser Scanner?
A handheld 3D laser scanner is a portable device that allows users to move freely while scanning the surface of objects to generate their three-dimensional digital models.
This type of scanner measures the shape and dimensions of an object by emitting a laser and capturing the reflected light signals.
These point clouds can be interpolated into the surface shape of the object. The denser the point cloud, the more accurate the resulting model, leading to more precise 3D reconstruction.
If the scanner captures the surface color, texture mapping can be applied to the reconstructed model.
Handheld 3D laser scanners are compact, lightweight, and flexible, making them ideal for scanning smaller objects, complex shapes, or hard-to-reach areas.
They excel in analyzing and reporting geometric dimensions and tolerances (GD&T), with generated STL files easily imported into inspection software for quick editing and subsequent processing.
These scanners efficiently capture 3D data from various angles and complex environments, providing effective 3D reconstruction and analysis capabilities.
What Can 3D Laser Scanners Do?
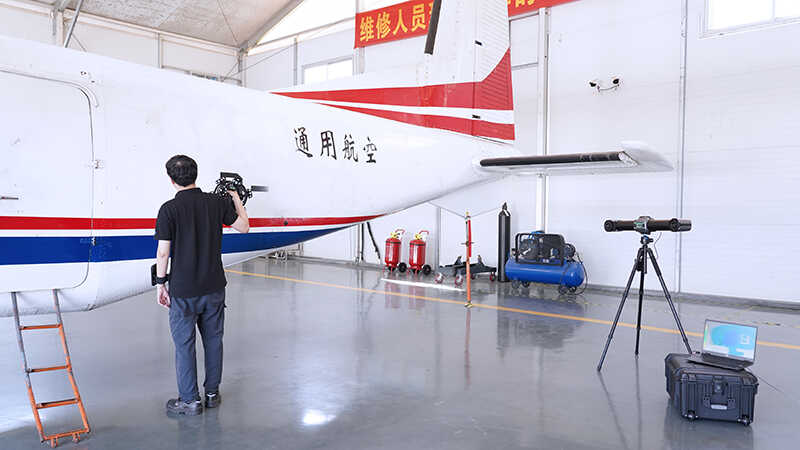
3D laser scanners are capable of scanning a wide range of objects, regardless of their geometric shapes, sizes, materials, or surface finishes. Professional 3D laser scanners can even handle very large objects, human bodies, and buildings.
Portable and handheld scanners offer flexibility, allowing operators to perform precise 3D measurements in any environment, whether it’s components in a production workshop, excavated pipelines, or hard-to-reach tiny parts.
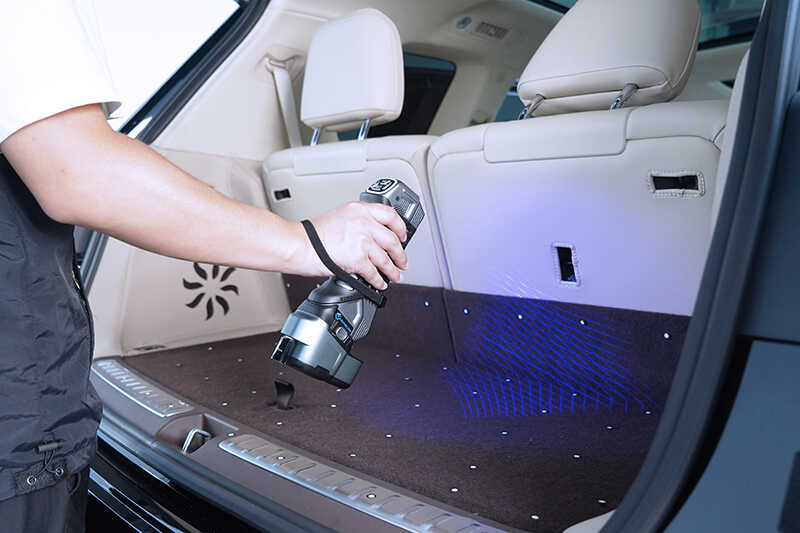

Since their inception, 3D laser scanners have been used primarily to measure large objects that are difficult to measure manually.
Technical Features of 3D Laser Scanners
• Automated Data Collection with One-Button Operation
3D laser scanners are highly automated, capable of performing one-button scans without manual intervention. The instrument automatically emits lasers to measure the 3D coordinates of the target object’s surface, simplifying the operation process.
• High-Speed Scanning (Up to 1 Million Points per Second)
The scanning speed of Scantech SIMSCAN-E 3D laser scanners can reach up to 3million points per second, significantly enhancing data acquisition speed.
Compared to traditional methods, which typically require 2-5 seconds to measure a single point (and even minutes in complex scenarios), the high speed of 3D laser scanners makes measurements in intricate fields such as historical buildings, factory pipelines, tunnels, and terrains both feasible and efficient.
• Comprehensive Data Collection with High Density and Precision (Millimeter-Level Accuracy)
3D laser scanners quickly acquire high-precision, high-resolution point data in both horizontal and vertical directions. All visible objects on-site, except for glass, water, and mirror-reflective surfaces, can be accurately scanned.
• Non-Contact Measurement Ensuring Safety
3D laser scanners use non-contact measurement methods, eliminating the need to touch the object being measured and reducing measurement risks.
This method is particularly suitable for measuring complex structures in hazardous environments (such as high-altitude locations, power plants, and radiation areas), providing a safety advantage.
• Excellent Digital Compatibility
The data collected by the scanner is fully digital, facilitating post-processing and output. Additionally, it is compatible with 3D software, enhancing data sharing and processing convenience.
Which Sectors Benefit from 3D Laser Scanners?
3D laser scanners have a broad range of applications, spanning nearly every industry.
Here are the main application areas and their specific uses:
| Industry | Specific Uses |
| Aerospace | – Accurate measurement and modeling of complex components – Ensuring aircraft performance and safety |
| Transportation and Automotive | – Design and quality control – Enhancing precision in maintenance and manufacturing |
| Consumer Goods | – Product design and prototyping – Providing high-precision data to accelerate development |
| B2B Manufacturing | – Optimizing production processes – Quality inspection and manufacturing precision assurance |
| Heavy Industry | – Facility and equipment maintenance management – Increasing production line efficiency |
| Healthcare | – Creating personalized medical devices, such as prosthetics – Rapid and accurate measurement of physical characteristics |
| Heritage, Arts, and Architecture | – Preservation and research of cultural artifacts – Creating digital models to support virtual displays and restoration |
3D laser scanning technology demonstrates significant advantages across various stages, including design, prototyping, engineering, production, quality control, and distribution. Its high precision, ease of use, and multifunctionality make it an invaluable tool in numerous fields.
Features to Consider When Choosing a 3D Scanner
Scanning Accuracy
Scanning accuracy refers to how close the measurements captured by the scanner are to the true dimensions of the object being scanned.
It is typically measured in units such as millimeters (mm) or microns (µm). Higher accuracy means the scanner produces measurements that more precisely match the actual dimensions of the object.
Level of detail, often referred to as resolution, indicates how finely the scanner can capture small features or intricate details on the object. It’s the smallest possible distance between two points in the scan.
The finer the resolution, the more detail the scanner can capture. Resolution is a key factor for applications requiring fine detail, such as digitalizing archaeological artifacts or high-end manufacturing.
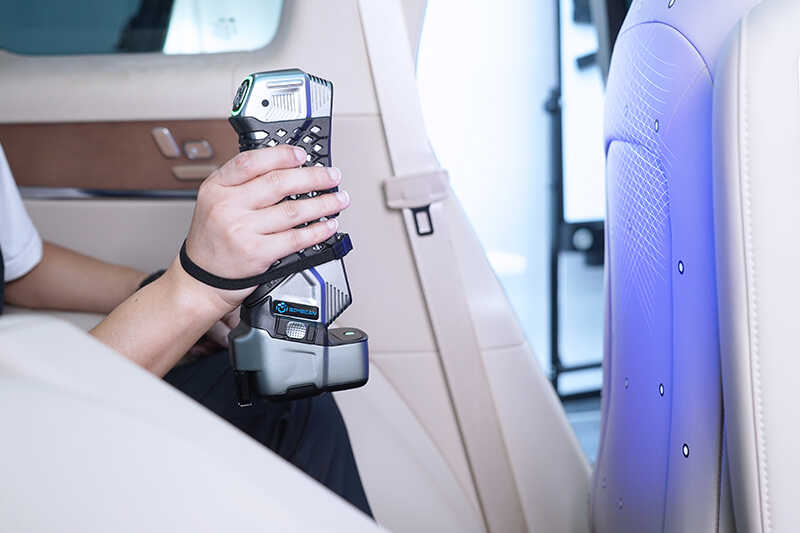

Scanning Range
Scanning range defines the maximum area that the scanner can capture in a single scan. For applications involving large objects or extensive areas, a scanner with a broad range is essential.
Note that there is often a trade-off between range and resolution; a larger range may reduce resolution.
Scanning Speed
Scanning speed is typically expressed in points per second (pps) or frames per second (fps) and reflects the amount of data the scanner can capture within a given time.
Higher scanning speeds can significantly reduce the time required for scanning, especially for complex or large objects. However, speed may sometimes affect accuracy, so finding a balance based on specific needs is crucial.

Operating Distance
Operating distance refers to the optimal distance between the scanner and the object being scanned. This parameter directly affects the accuracy and quality of the scan results.
For scenarios requiring scans at various distances, a scanner with flexible operating distances would be more suitable.
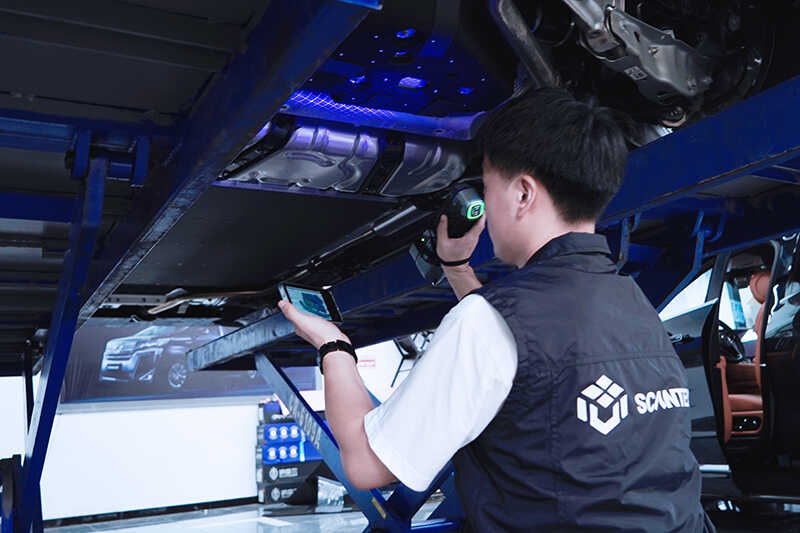
Portability
Depending on your application, the weight and portability of the scanner may be important factors. If scanning in multiple locations or outdoors, a lightweight and easily portable scanner can make your work more convenient.

Software
Compatibility 3D laser scanners typically require specialized software for processing and analyzing scan data. Ensuring that the scanner is compatible with your operating system and commonly used software is essential. Some high-end models come with powerful data processing software, enhancing your workflow efficiency.
Power Requirements
Considering the power requirements of the scanner is important, especially when working outdoors or in environments without direct power sources. Some scanners are equipped with built-in batteries, making them more convenient for fieldwork.
Additional Features
Additional features such as automatic alignment, wireless connectivity, and color capture can enhance the convenience and versatility of the scanner. For users requiring diverse operations in varying environments, these features can significantly boost efficiency.
How Much Do 3D Laser Scanners Cost?
The price of 3D laser scanners varies significantly based on their performance, brand, and application. Generally, prices can range from several thousand to hundreds of thousands of dollars. Here is a rough price range for different tiers of 3D laser scanners:
Entry-Level Scanners ($5,000 – $15,000)
These are suitable for scanning small objects or tasks with lower accuracy requirements. Typically used in education, preliminary design concepts, or simple reverse engineering projects. These scanners often have lower resolution and a smaller scanning range.

Industrial and Professional Scanners ($15,000 – $150,000)
Industrial-grade scanners are used for tasks requiring the highest precision, such as high-accuracy quality control, and highly complex reverse engineering projects.
These devices generally offer extremely high scanning precision, resolution, and speed, and support a wide range of application environments.
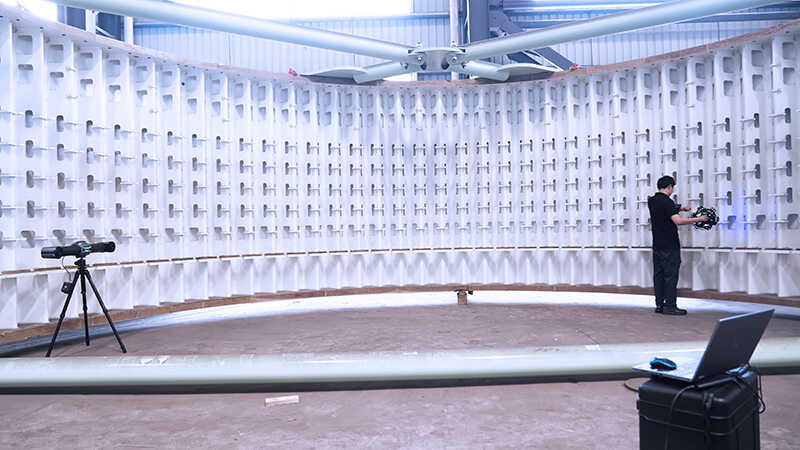

Using low-cost 3D scanners in professional applications can be a significant mistake. While budget-friendly devices may save costs in the short term, they often lack the precision, resolution, and stability required.
This can result in inaccurate data, project rework, and potentially higher subsequent costs. In high-demand industries, selecting a high-quality 3D scanner that meets specific requirements is crucial for ensuring project success.
What is the Future of 3D Scanning?
The accessibility and affordability of 3D scanners are improving, and as technology matures, reduced costs are enabling more users to utilize these tools, especially in product development and quality control.
The adoption of automated quality control is also on the rise, with many companies beginning to use 3D scanners and automation kits to enhance efficiency and precision.
Additionally, the performance levels of 3D scanners continue to improve, with integrated 3D scanning software further enhancing measurement accuracy and efficiency.
Improved usability and ergonomic design make these devices accessible to operators of all skill levels, making them especially attractive in a competitive labor market.
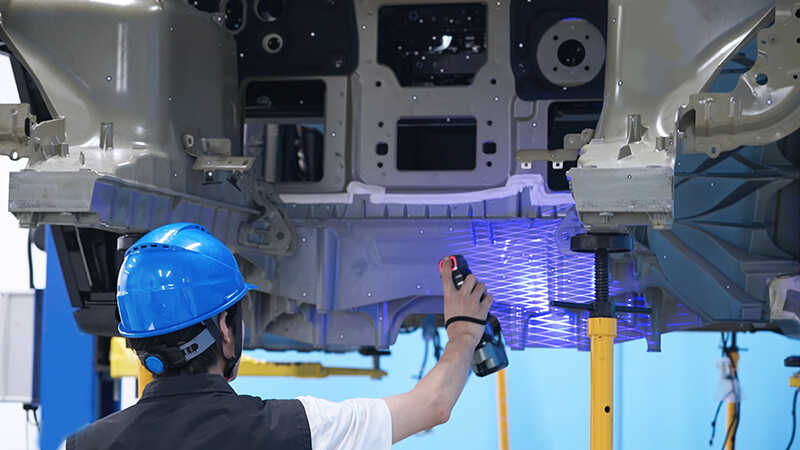

What Sets Scantech Apart
What sets Scantech apart is its seamless integration of cutting-edge technology and craftsmanship, focusing on producing the most reliable industrial-grade products.
The company’s experienced engineering team works closely with clients to deeply understand project goals and develop solutions that meet industry demands.
Scantech’s 3D scanners are not only user-friendly but are also calibrated before leaving the factory, ensuring that users can quickly perform high-precision 3D scans.
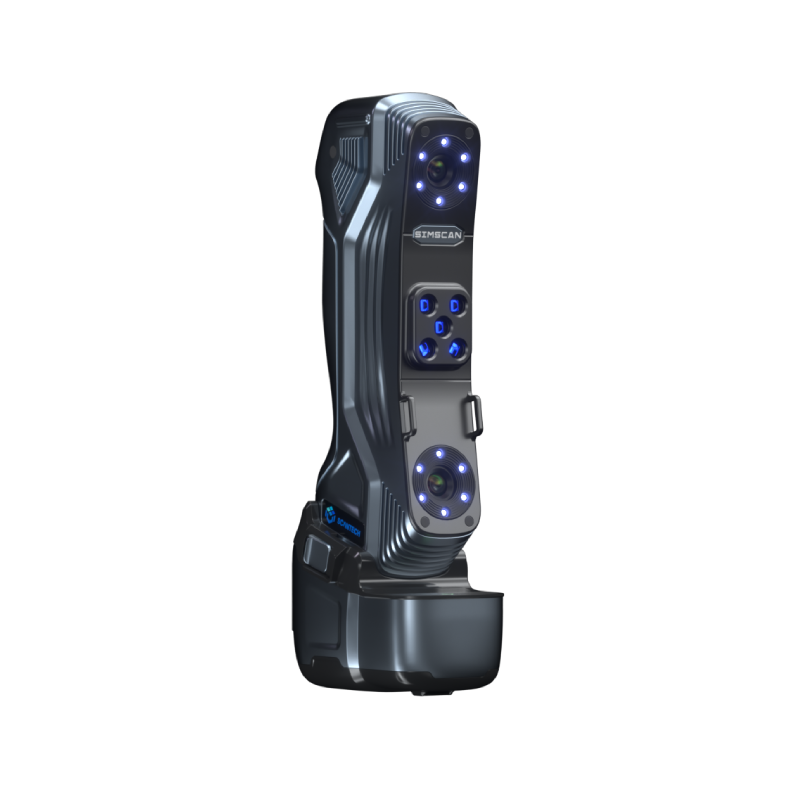
For example, the SIMSCAN is a palm-sized 3D scanner introduced by Scantech, weighing just 570 grams, and equipped with a metrology-grade measurement system capable of capturing every detail and constructing 3D models swiftly.
The SIMSCAN, with its high frame rate and rapid data capture capabilities, delivers high-quality scans even in confined spaces like engine bays. Its design won the Red Dot Design Award in 2021, highlighting Scantech’s leadership in innovative design.
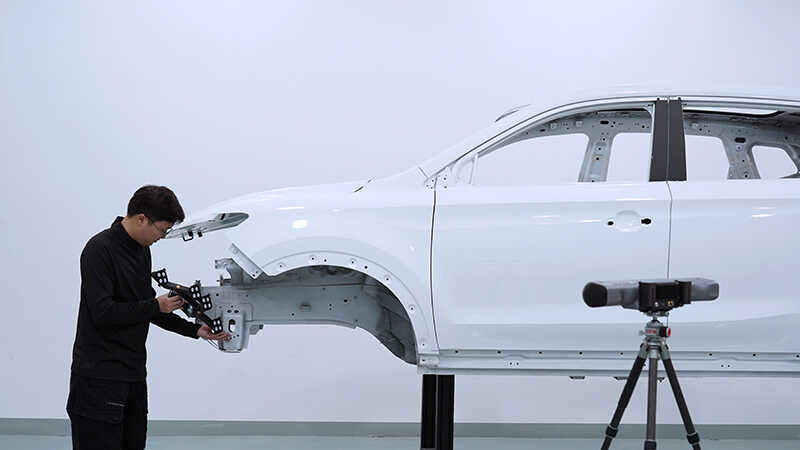

Additionally, Scantech produces a range of scanners for various applications and includes the proprietary Scantech 3D software, which provides real-time feedback during scanning and integrates into the product redesign process.
The iReal M3 3D color scanner, is considered an ideal choice for body scanning. Meanwhile, the NimbleTrack wireless 3D scanning system, launched in April 2024, can scan objects of all sizes in any environment.
It tackles challenging scenarios such as field measurements of corroded oil pipelines or high-altitude scanning of large components.
The NimbleTrack can also be paired with the tracking i-Probe to probe hard-to-reach areas, making it a valuable tool in industrial applications.
























 All Products
All Products 











 en
en 












