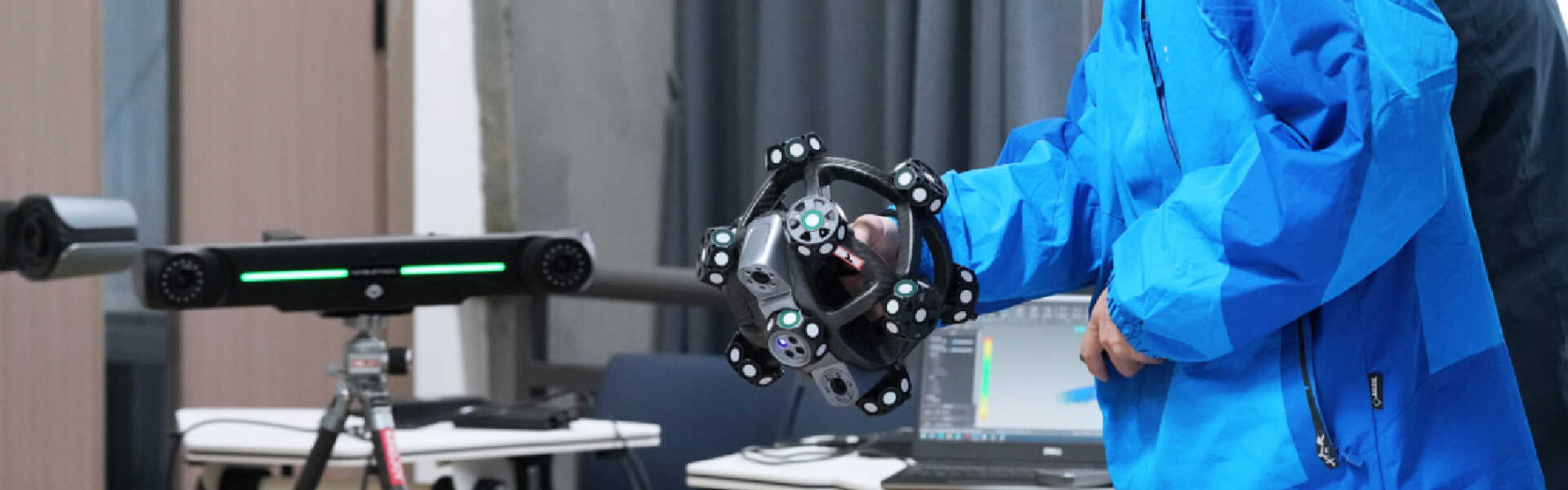
How 3D Scanning is Shaping the Future of Education
The Future of Jobs Report 2023 by the World Economic Forum highlights a critical point: by 2027, 44% of workers’ skills will be disrupted due to technology adoption.
This rapid shift calls for an educational transformation that focuses on digital learning tools to prepare students for a job market that is increasingly defined by automation, AI, and new forms of digital technology.
In particular, 3D scanning offers a unique opportunity. In industries like engineering, manufacturing, and healthcare, 3D scanning technology is not just useful but vital.
Whether it’s scanning a part for inspection or modeling for design, hands-on experience with this tool can give students a significant advantage in the future workforce.
The Role of 3D Scanning in Education
SCANTECH is enhancing education through partnerships with universities, where we help set up establish joint teaching labs, provide training and seminar support, and create opportunities for talent development.
These collaborations offer students hands-on experience with 3D scanning technology, allowing them to learn both the fundamentals of 3D data capture and its advanced applications in industries like automotive, aerospace, and healthcare.

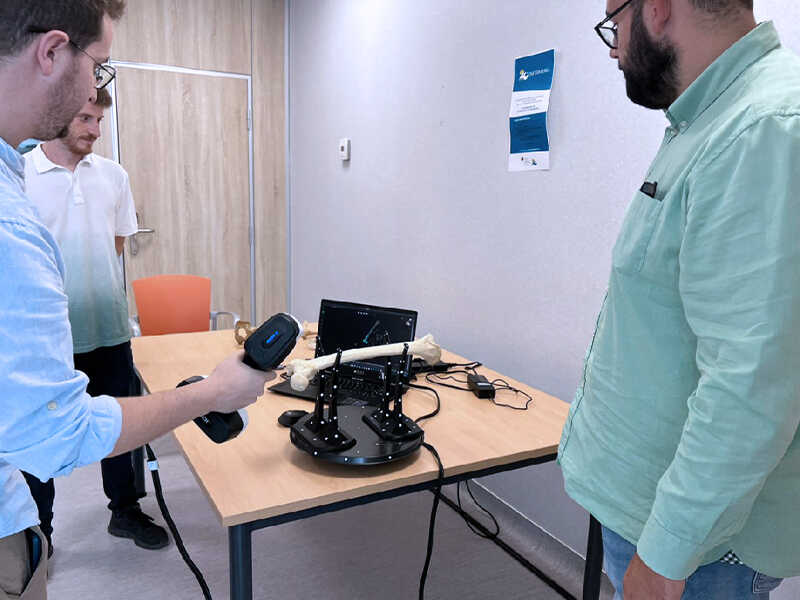
3D Scanning for Medical Education
The project at the CEU Cardenal Herrera University aims to create a virtual bone repository for medical students, providing detailed learning materials through 3D scanning.
Using SCANTECH’S 3DeVoK color 3D scanner, bone specimens are captured from multiple angles to ensure precision, including fine details like gaps and holes. The data is then processed in 3D software to generate accurate models.
These models are further enhanced through VR and AR, allowing for immersive learning experiences. Additionally, 3D printing is used to create physical models, offering hands-on interaction with bone structures.

3D Scanning for Automotive Education
At the University of Ho Chi Minh City (IUH), 3D scanning is transforming automotive reverse engineering. Using Scantech’s TrackScan-Sharp, students and instructors quickly capture high-precision 3D data of car frames, overcoming the challenges of manual measurement and rusted or complex structures.
This technology accelerates the modeling process by efficiently extracting features and creating accurate CAD models, significantly improving productivity and accuracy in automotive design.
Seminar on Advancing 3D Scanning
To foster innovation, it’s crucial for academic institutions and industries to collaborate closely. Programs such as the Industry-Education Integration Seminar held at Zhejiang University provide a platform for sharing knowledge and discussing the latest technological advancements.
These initiatives not only focus on talent development but also align academic curriculums with the fast-evolving needs of industries.
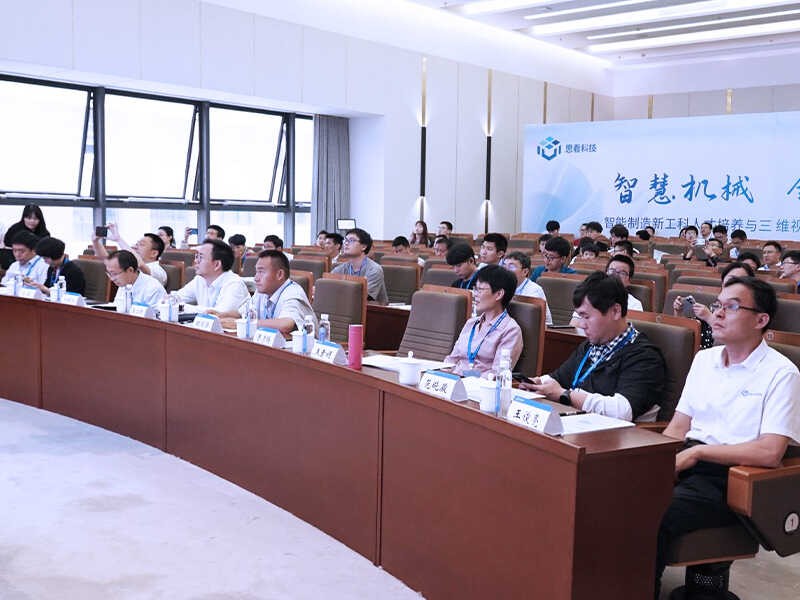

At these seminars, experts and scholars discuss the latest trends in intelligent manufacturing, including 3D digitization. Students are encouraged to engage in scientific and technological innovation projects, internships, and enterprise-led classrooms.
Such opportunities help students connect theory with practice, deepening their understanding and fostering collaboration between academia and industry.
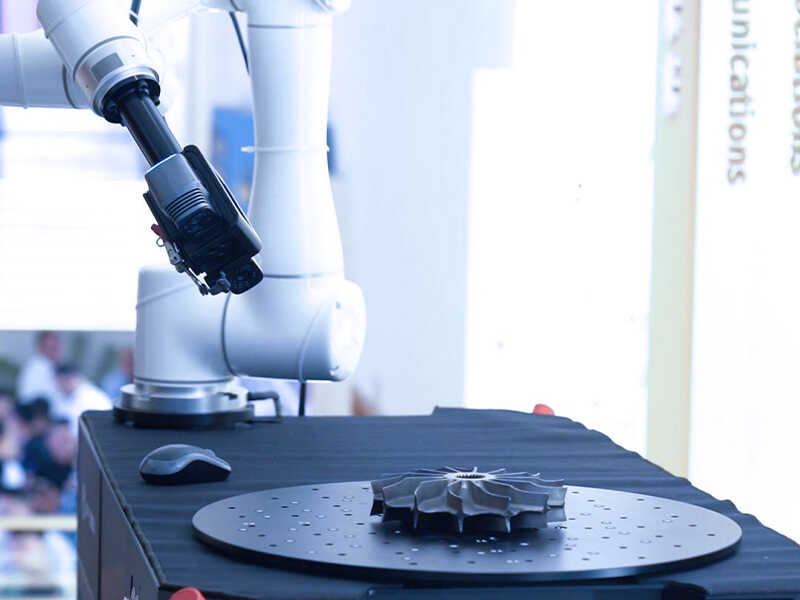

Practical Learning
One of the most impactful ways that 3D scanning is enhancing education is through practical learning.
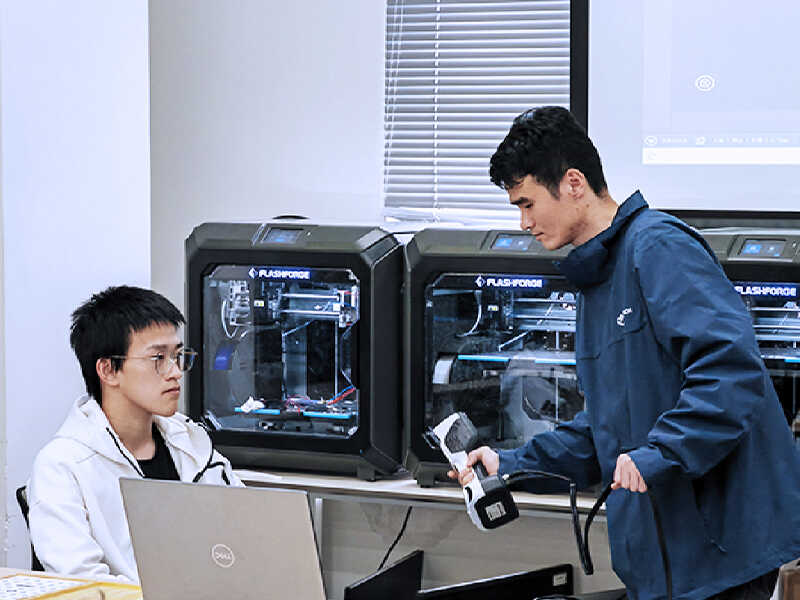
For instance, students at the Shanghai Jiao Tong University, use 3D scanners like the KSCAN-Magic to collect data and use 3D software for assisted modelling, enabling them to practice real-world applications of their learning.
These 3D scanning training covers a wide range of key areas, including:
● Basic principles of 3D scanning
● 3D software operation
● Industrial applications of 3D scanning
● Collect 3D data of objects
● Use 3D software for assisted modeling
3D Scanning in Vocational Education
In addition to university-level education, 3D scanning is also playing a pivotal role in vocational education.
Competitions like the Chinese Vocational Skills Competition for Electronic Information Service have introduced automated 3D inspection systems like the AM-DESK to test students’ skills in programming, automated scanning, and 3D data acquisition.
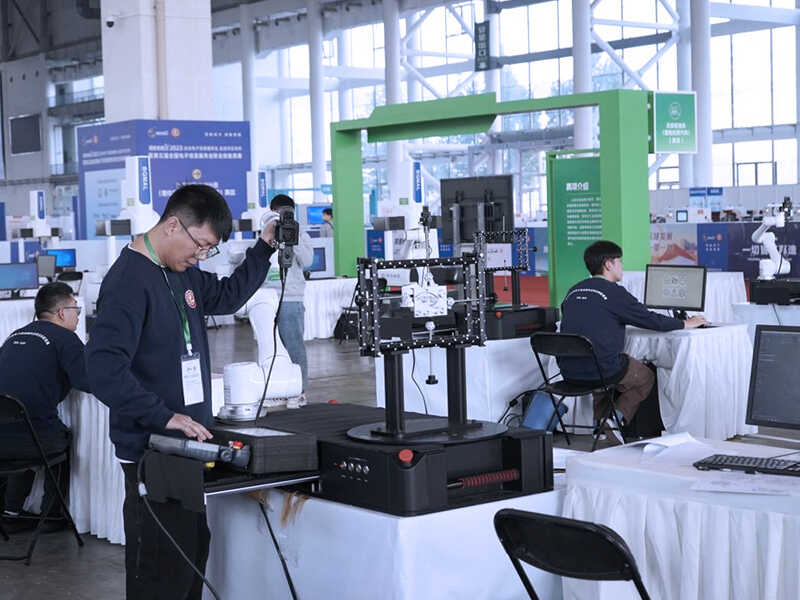

These competitions offer students the chance to apply their technical knowledge in a competitive setting, honing their skills and preparing them for careers in industries such as manufacturing and electronics.
Moreover, they gain exposure to the latest tools and technologies, ensuring they are ready for the future job market.
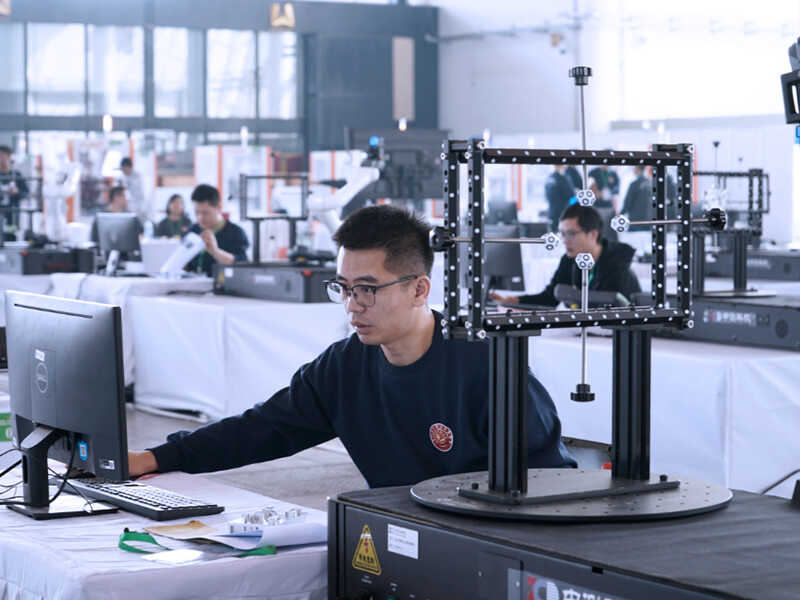

Competition Support
In addition, collaborations with industry partners allow students to engage in projects like Formula Student China, where university teams use 3D scanning to improve racing car designs.
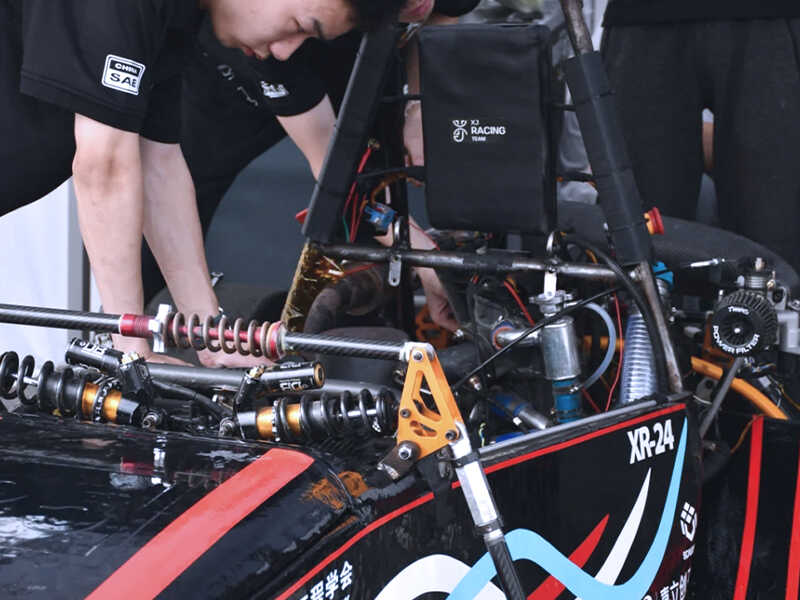
By scanning components like frames and aerodynamic parts, students gain insights into structural integrity and performance enhancements that would otherwise be out of reach.
The introduction of 3D scanning technology to international competitions, such as the 46th WorldSkills Competition, marks a significant milestone in global education.
The use of advanced 3D scanning systems like the SIMSCAN Portable 3D Scanner enabled contestants to create precise 3D models for additive manufacturing, highlighting the importance of this technology in skill development and education worldwide.
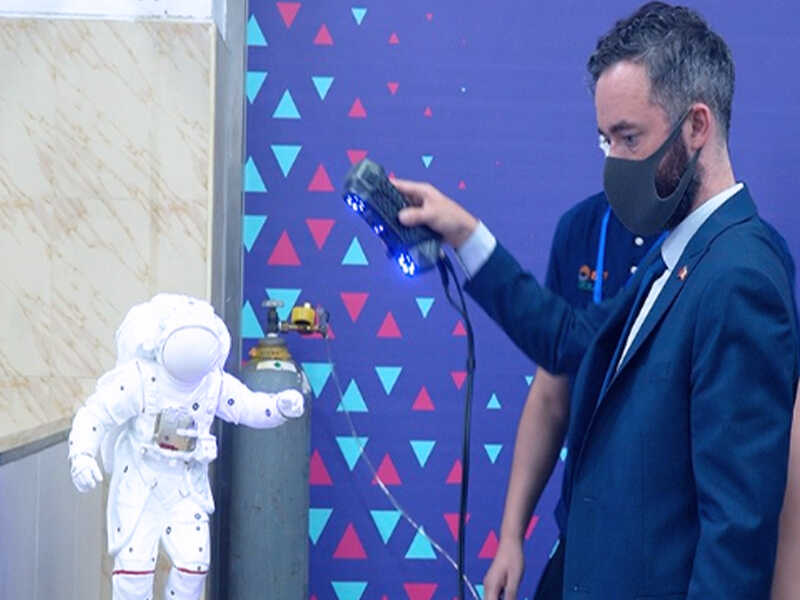

The global reach of these competitions demonstrates the growing significance of 3D scanning as a vital skill across industries. By offering students exposure to these technologies, educational institutions help shape a generation of workers who are ready to meet the challenges of tomorrow’s job market.
A Vision for the Future
As we look to the future, the integration of 3D scanning technology into education is not just about keeping up with technological trends but driving innovation forward.
By building joint research stations, such as the Postdoctoral Workstation of Zhejiang Province, SCANTECH and universities are creating an ecosystem of research and innovation that supports the development of cutting-edge technologies and fosters talent growth.
In particular, the application of 3D scanning technology in fields like cultural heritage preservation, where spatial information is combined with technology to protect and promote our history, is a perfect example of how education and technology can work together to preserve and enrich the world we live in.
Conclusion
The future of education is deeply intertwined with the advancement of technology. 3D scanning, with its applications in design, engineering, healthcare, and beyond, is essential in shaping the next generation of professionals.
By integrating this technology into educational models through industry collaborations, hands-on learning, and real-world applications, we can prepare students to meet the demands of an ever-evolving job market.
Through initiatives that bridge the gap between academia and industry, we are laying the groundwork for a future where education is not just about learning concepts, but about developing practical, future-ready skills that will define the workforce of tomorrow.

























 All Products
All Products 











 en
en 













