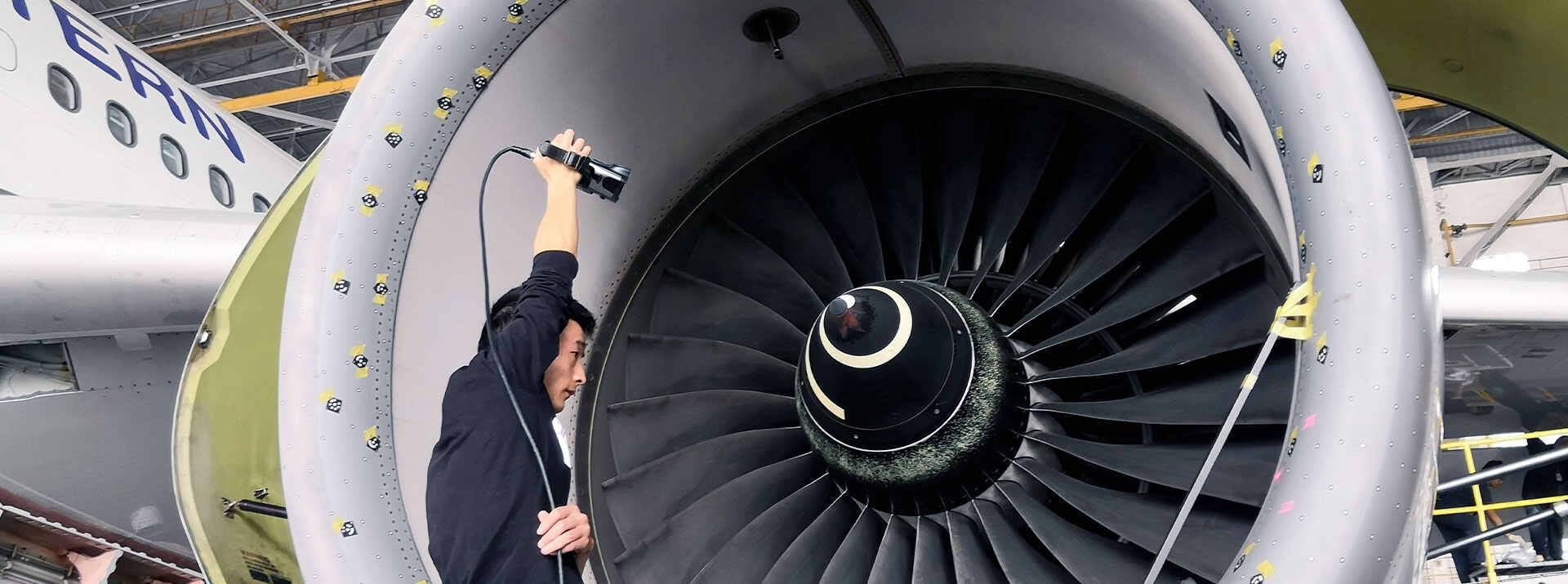
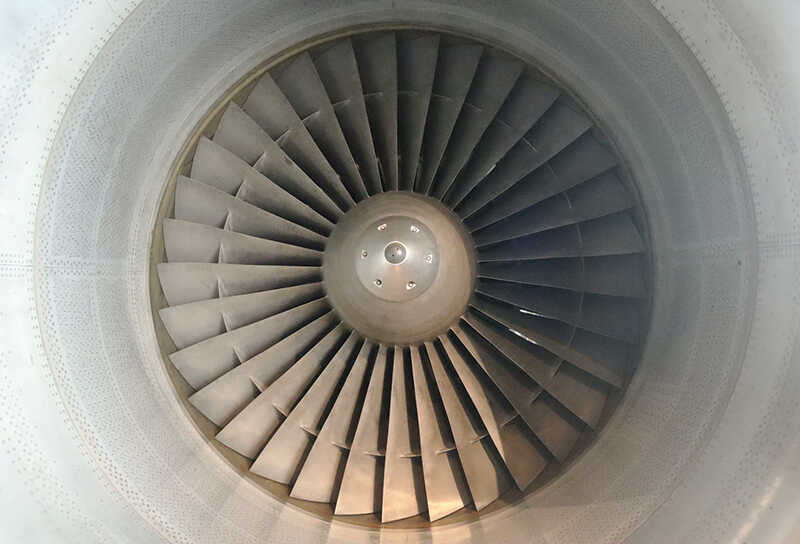
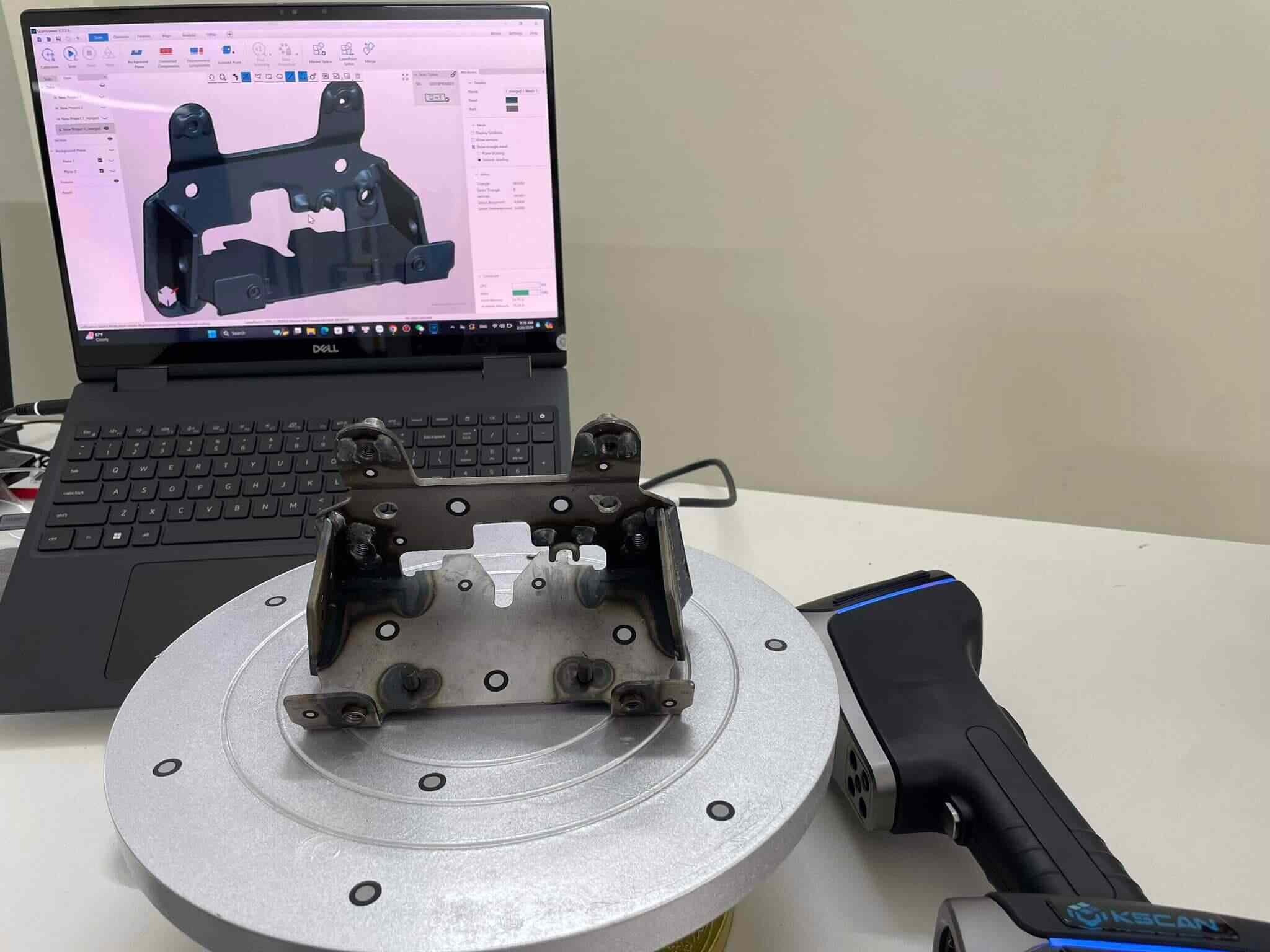
Have you ever scanned a large-size sculpture, or object, and the measurement results are a total disaster? Scanning large-size objects can be challenging as errors accumulate over a certain distance during measurement.
How can we eliminate accumulated errors? By integrating photogrammetry with 3D scanning, we can enhance the speed and accuracy of data collection and the 3D modelling process.
What’s photogrammetry?
The word “Photogrammetry” was coined by Prussian architect Albrecht Meydenbauer in his article “Die Photometrographie” in 1867. Photogrammetry develops from plane table, analogy, analytical to digital photogrammetry. Each phase of its development extends about 15 years. In this blog, we mainly focus on digital photogrammetry.
Photogrammetry is a measuring technique that takes photographs from different perspectives to obtain 3D coordinates. Specifically speaking, it extracts geometric information by triangulating the locations of points on the subject.
Photogrammetry software can find characteristic points that are repeated in photos. The distance of these points can be inferred using triangulations. The more photos we take from different angles, the more accurate these locations are. Finally, these points would be converted into a mesh and a 3D model.
How does photogrammetry work?
Photogrammetry can utilize images from aerial photography among other sources, offering enhanced accuracy and depth by analyzing multiple photographs taken from various vantage points, not limited to aerial views. While aerial photography serves to capture images providing a general overview of terrain, photogrammetry delves deeper, offering meticulous measurements of distance, area, and direction, surpassing the inherent positional errors found in traditional aerial imagery.
The essence of photogrammetry lies in its utilization of multiple overlapping photographs taken from diverse vantage points and angles. Through intricate analysis and correlation of these images, photogrammetry reconstructs a 3D representation of the scene, extracting precise spatial data with remarkable fidelity.
This method finds extensive application across various disciplines such as architecture, engineering, surveying, and quality control, where exactitude in measurement is paramount. By leveraging the synergy between advanced imaging techniques and computational algorithms, photogrammetry emerges as an indispensable tool for capturing and quantifying the intricacies of our physical environment with unparalleled accuracy and efficiency.
Photogrammetry for engineering
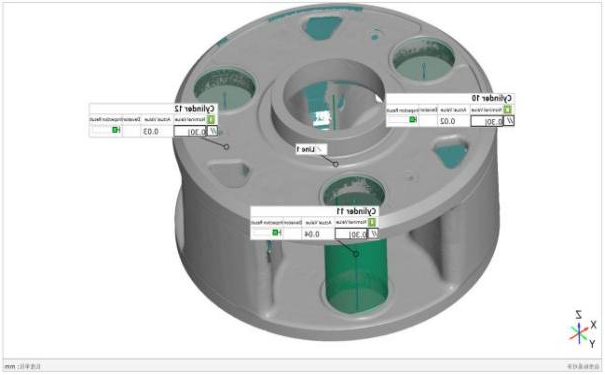
In metric photogrammetry, engineers prioritize precision, leveraging necessary points over pixel counts for tasks like quality control and reverse engineering. This method extracts accurate measurements and positions from images using precision algorithms and key points to build models.
Photogrammetry delivers exact, efficient solutions for surveying, designing, analyzing, and documenting. It’s vital in engineering for creating detailed maps, models, and orthophotos for infrastructure and environmental assessments. It also produces accurate documentation of existing structures, aiding renovations and maintenance.
Additionally, photogrammetry enhances design and visualization with 3D models, identifies conflicts, and cuts costs. It monitors construction, checking for deviations to maintain quality and safety.
How can photogrammetry be used in 3D scanning?
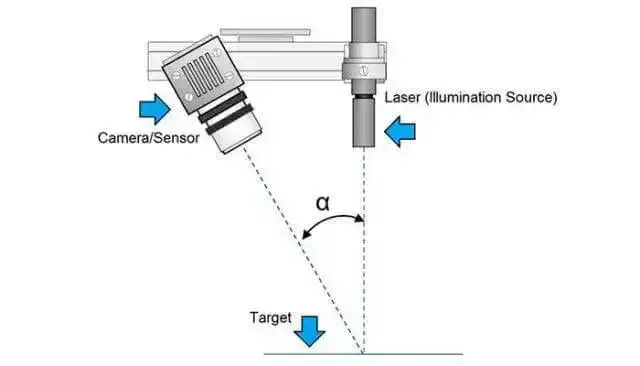
The 3D laser scanner uses lasers to scan the geometry of an object and obtain its 3D data. Once all the points are captured, a dense point cloud is generated, which can be used to create a 3D model.
Most 3D scanners on the market are capable of scanning objects whose sizes are within a range of 1 m, while it is difficult for these 3D scanners to scan large-scale objects like wind turbines, planes, and buildings. There is where photogrammetry comes in.
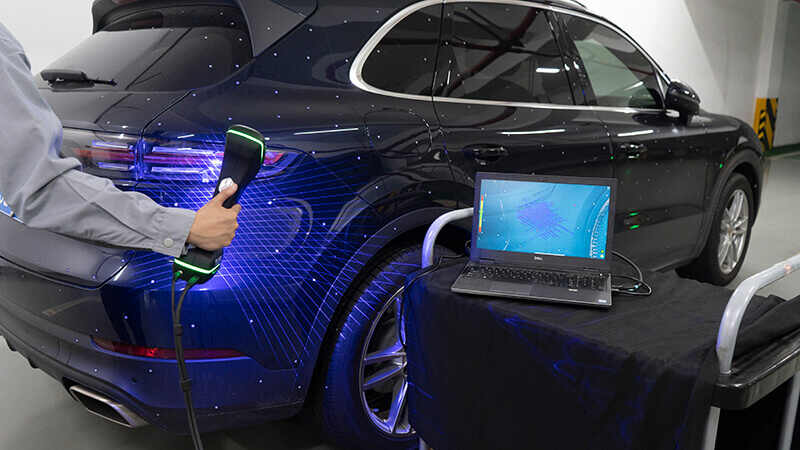
When measuring an object with photogrammetry, the first step is to put reflective markers on the object surface and coded targets around it. A scale bar is also necessary to serve as a reference. Then, shots are taken from different perspectives, while making sure that you take photos that overlap.
These photos will help to construct a general 3D geometry of the object. The details of the object’s surface then can be captured using a 3D scanner.
With high-resolution and full-frame cameras, a photogrammetry system can give you the highest quality output. Thanks to its large shooting area and precise algorithms, it can reduce errors of connection that accumulate over distance.
How can Scantech help?
Scantech offers MSCAN photogrammetry system for scanning large-scale objects, with high requirements in accuracy and measurement repeatability. MSCAN photogrammetry system can work alone, or work with handheld 3D scanners, to achieve a volumetric accuracy of up to 0.015 mm/m.
























 All Products
All Products 











 en
en